
Assess each patient's risk before prescribing, and monitor for development of these behaviors and conditions. Hydrocodone bitartrate and acetaminophen has the potential for addiction, abuse, and misuse, which can lead to overdose and death. Limit dosages and durations to the minimum required and follow patients for signs and symptoms of respiratory depression and sedation. Reserve concomitant prescribing for patients with inadequate alternative treatment options. Concomitant use of benzodiazepines and opioids may result in profound sedation, respiratory depression, coma, and death.

Acetaminophen has been associated with cases of acute liver failure, at times resulting in liver transplant and death, most often with the use of acetaminophen at doses that exceed 4000 mg/day, and involving more than 1 acetaminophen-containing product. Monitor patients receiving hydrocodone bitartrate and acetaminophen oral solution and any CYP3A4 inhibitor or inducer for signs of respiratory depression or sedation. Prolonged use of hydrocodone bitartrate and acetaminophen oral solution during pregnancy can result in neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome, which may be life-threatening if not recognized and treated. Accidental ingestion of hydrocodone bitartrate and acetaminophen oral solution, especially by children, can result in a fatal overdose of hydrocodone bitartrate and acetaminophen. Monitor closely, especially upon initiation or following a dose increase. Serious, life-threatening, or fatal respiratory depression may occur. To ensure that the benefits of opioid analgesics outweigh the risks of addiction, abuse, and misuse, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has required a Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS) for these products.

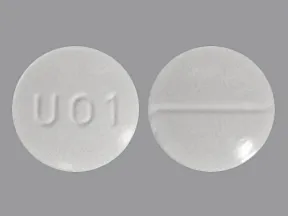
Hydrocodone bitartrate and acetaminophen oral solution has the potential for addiction, abuse, and misuse, which can lead to overdose and death.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
